
20 Oct What is AR?
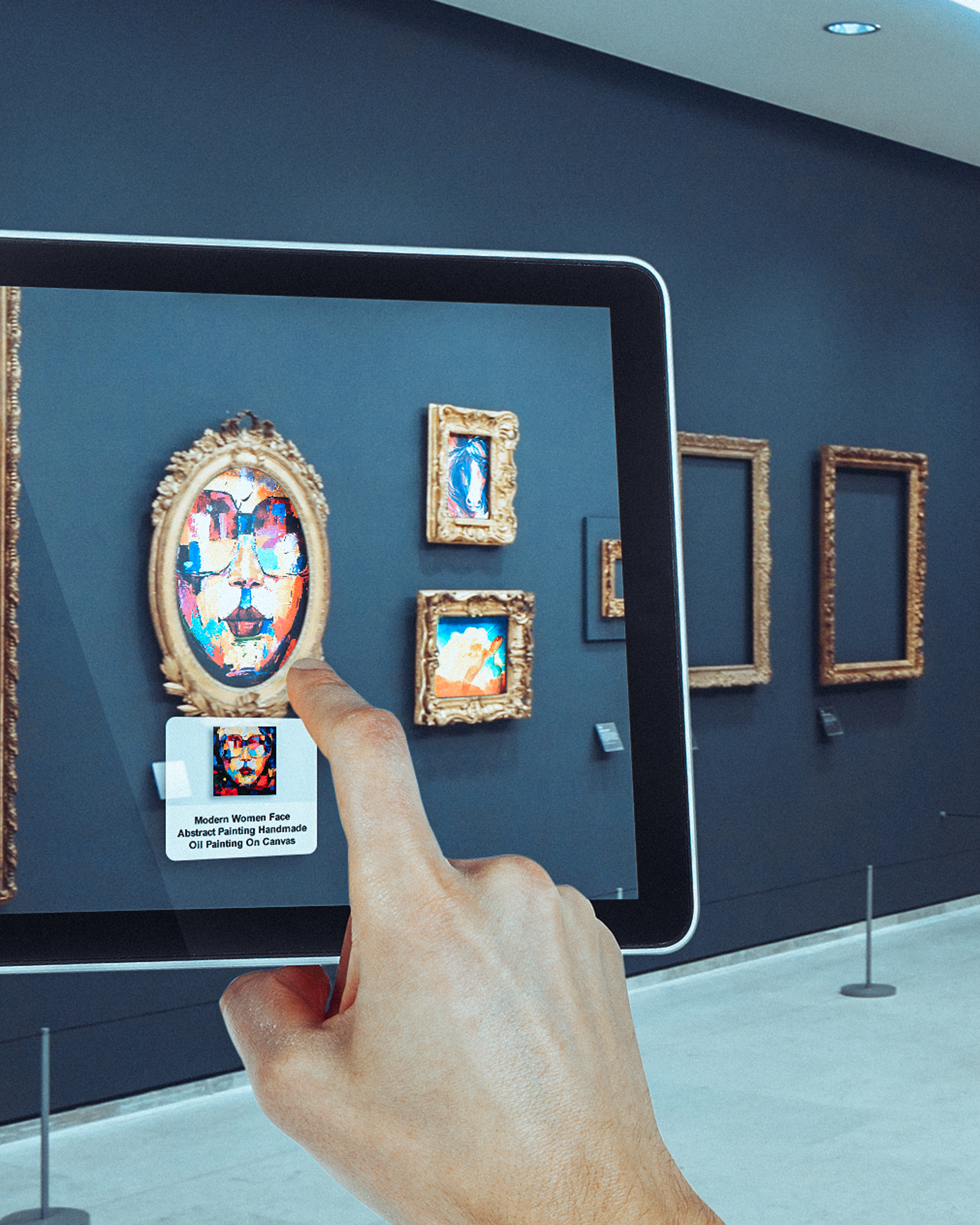
Augmented Reality (AR) is a real-time direct or indirect view of a physical real-world environment that has been enhanced/augmented by adding virtual computer-generated information to it. AR is both interactive and registered in 3D as well as combines real and virtual objects. Milgram’s Reality-Virtuality Continuum is defined by Paul Milgram and Fumio Kishino as a continuum that spans between the real environment and the virtual environment comprise Augmented Reality and Augmented Virtuality (AV) in between, where AR is closer to the real world and AV is closer to a pure virtual environment.
Augmented reality is used to either visually change natural environments in some way or to provide additional information to users. The primary benefit of AR is that it manages to blend digital and three-dimensional (3D) components with an individual’s perception of the real world. AR has a variety of uses, from helping in decision-making to entertainment.AR delivers visual elements, sound and other sensory information to the user through a device like a smartphone or glasses. This information is overlaid onto the device to create an interwoven experience where digital information alters the user’s perception of the real world. The overlaid information can be added to an environment or mask part of the natural environment.
Top AR use cases
AR can be used in the following ways:
- Retail. Consumers can use a store’s online app to see how products, such as furniture, will look in their own homes before buying.
- Entertainment and gaming. AR can be used to overlay a virtual game in the real world or enable users to animate their faces in different and creative ways on social media.
- Navigation. AR can be used to overlay a route to the user’s destination over a live view of a road. AR used for navigation can also display information about local businesses in the user’s immediate surroundings.
- Tools and measurement. Mobile devices can use AR to measure different 3D points in the user’s environment.
- Architecture. AR can help architects visualize a building project.
- Military. Data can be displayed on a vehicle’s windshield that indicates destination directions, distances, weather and road conditions.
- Archaeology. AR has aided archaeological research by helping archeologists reconstruct sites. 3D models help museum visitors and future archeologists experience an excavation site as if they were there.
Examples of AR
Examples of AR include the following:
- Apple Measure app. The Measure app on Apple iOS acts like a tape measure by enabling users to select two or more points in their environment and measure the distance between them.
- Snapchat, Instagram and Tiktok. Social Media filters use AR to overlay a filter or mask over the user’s Snap or picture.
- Pokemon Go and other AR mobile games. Pokemon Go is a popular mobile AR game that uses the player’s GPS to detect where Pokemon creatures appear in the user’s surrounding environment for them to catch.
- Google Glass. Google Glass is Google’s first commercial attempt at a glasses-based AR system. This small wearable computer enables users to work hands-free. Companies such as DHL and DB Schenker use Google Glass and third-party software to enable frontline workers to be more efficient when it comes to global supply chain logistics and customized shipping. Google is also working on another pair of glasses in 2022 that’s designed to overlay a live transcription or translation of what another person says in text.
- U.S. Army. The U.S. Army uses AR in an eyepiece called Tactical Augmented Reality (TAR). TAR mounts onto the soldier’s helmet and aids in locating another soldier’s position.

No Comments